💡 LeetCode 94 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
💡 LeetCode 94 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
문제
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
입출력 예제
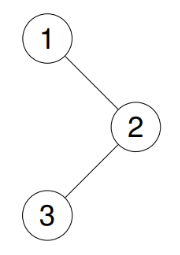
✅ 예제 1
1
2
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
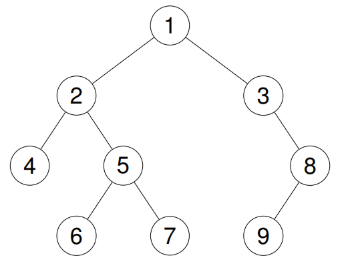
✅ 예제 2
1
2
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,2,6,5,7,1,3,9,8]
✅ 예제 3
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
✅ 예제 4
1
2
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
제약조건
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
작성 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// 1. 변수 선언 및 초기화
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode currentNode = root;
// 2. 주어진 노드가 모두 소요되거나 스택이 비었을 경우 종료
while (currentNode != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 왼쪽 노드로 이동
while (currentNode != null) {
stack.push(currentNode);
currentNode = currentNode.left;
}
// 스택 제일 위에 있는 노드 결과에 추가
currentNode = stack.pop();
result.add(currentNode.val);
// 오른쪽 노드로 이동
currentNode = currentNode.right;
}
// 3. 반환
return result;
}
}
- 굳이 최적화를 하자면
currentNode != null || !stack.isEmpty()조건의 순서를 바꾸는 것이다. if문은 단락 평가를 하므로 왼쪽 조건이true면 오른쪽 조건은 검사를 하지 않는다.Stack은 반복문을 도는 동안 비어 있는 순간이 없다.- 반면
currentNode는 왼쪽 노드 끝으로 이동했을 때마다null이 되므로 조건을 2개 검사하는 순간이 종종 발생한다. - 하지만 분기가 엄청 많은 트리가 아니라면 사실 큰 의미는 없다.
회고
- 로직을 짤 때 단락 평가 또한 고려해야겠다고 느꼈다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.